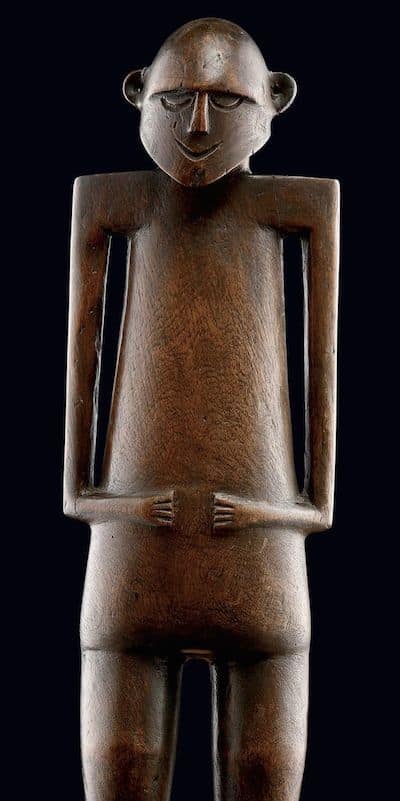
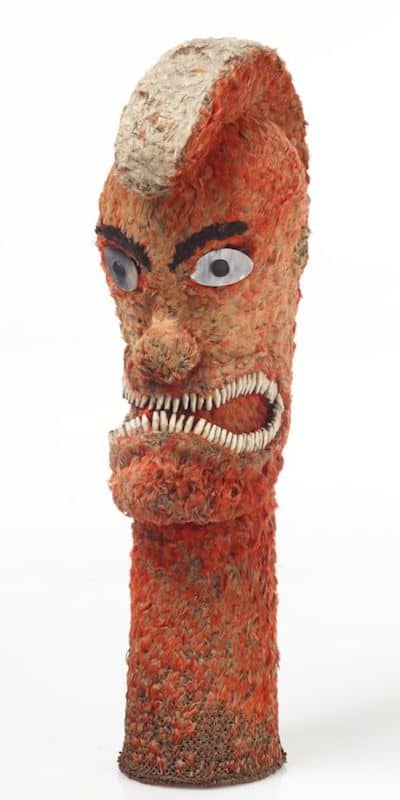
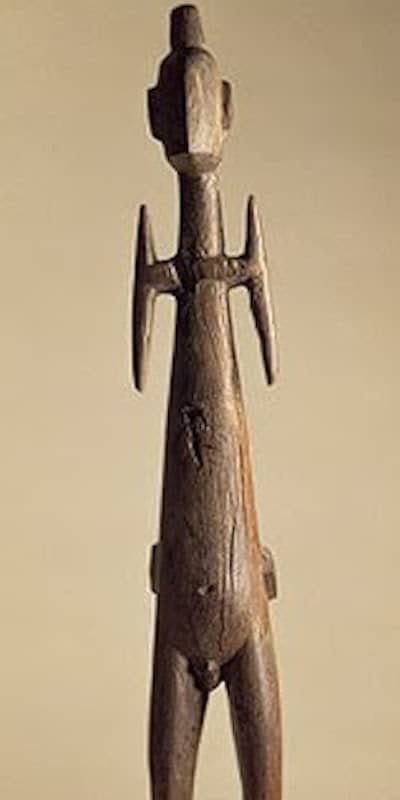
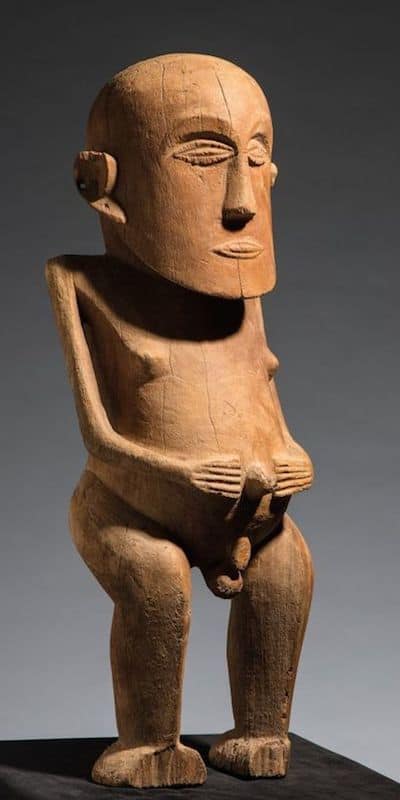
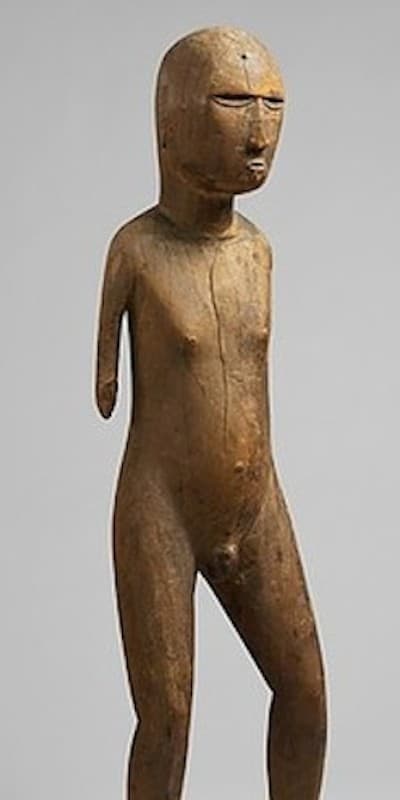
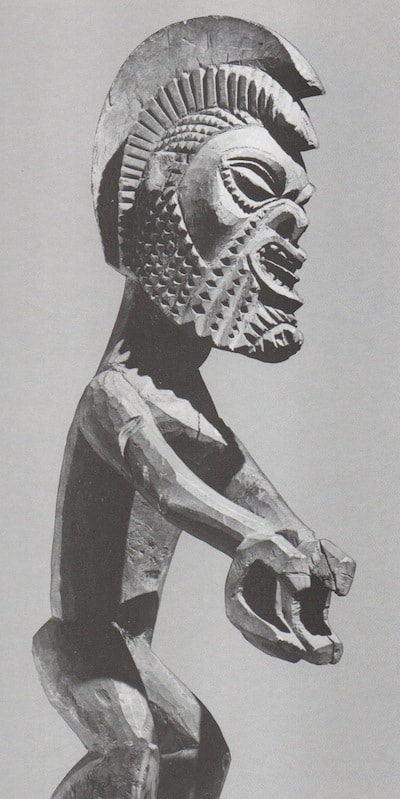
Oceanic Art
All the traditional arts from Polynesia Micronesia and Melanesia together form oceanic art. Melanesia is Papua New Guinea, Solomon islands, Vanuatu and New Caledonia. Polynesia is all the Pacific Islands like Tonga and Fiji but also includes New Zealand and Easter Island. Micronesia is just north of New Guinea.
This article helps to visually show some of the main types of Oceanic art. It aims to help the reader identify which region different Sculpture comes from.
Some authors consider Australian Aboriginal art as oceanic Art. Aboriginal Art though is different again and diverse enough to be considered in its own right.
Oceanic Art is some of the most valuable and sort after tribal art.
I Buy Old Oceanic art and Aboriginal Art. If you have a piece of Oceanic art to sell please contact me. If you want to know what your Oceanic art might be worth please send me a JPeg as I would love to see it.
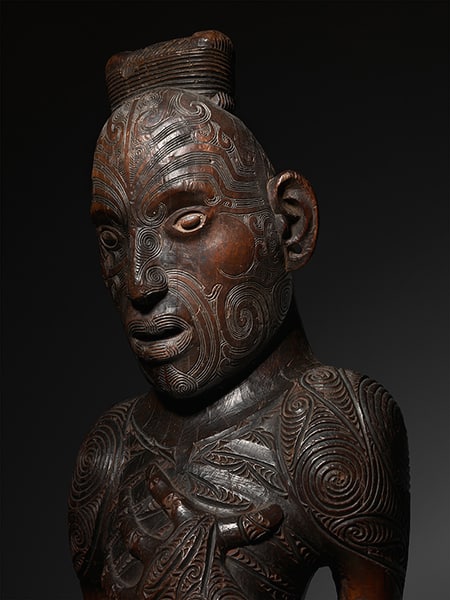

Oceanic Art facts
It is not possible to cover the vast amount of material about oceanic art in a single article. To simplify the matter this article deals with sculptures.
Oceanic Sculpture represented gods, deities or an ancestral hero. They were sometimes made free standing but are also often found as part of an object like the top of a fly whisk. Oceanic art also includes bowls weapons and Jewellery. These along with other artifacts are discussed in other articles.
Most pieces of oceanic Art have a spiritual side to them. Motifs and figures were carved on objects to make them more powerful.
Oceanic Art can vary in size from very small charms made to hide on your person to monumental stone monoliths.
The following is a visual guide to a few types of Oceanic Art but due to the huge variety throughout the Pacific, it is far from inclusive. It is probably better to think of this article as a brief introduction to this fascinating group of art forms. If you have a piece of Oceanic Art and want more detailed information about a particular piece please feel free to contact me.
“Oceanic Art is the sky, the bird. the dream” Andre Breton
Influence of oceanic art on Western Art
Oceanic art has had a major influence on the development of modern Western art. It strongly influenced the styles of Picasso Matisse and Vlaminck. It influenced many avant-garde painters and sculptors. Many of these artists were keen collectors of Oceanic art others frequented ethnographic museums.
The influence of Oceanic art coincided with changes that were taking place in Western art. Between 1870 and 1907 there was a gradual shift away from a perceptual mode of representation to a conceptual one. The “perceptual’ tradition which had dominated Western art since the Renaissance was coming to an end. This was in a large part due to photography being able to capture reality so effectively. Art was ready to evolve and indigenous art was a major catalyst. Indigenous art could present the essence of a subject and not just the physical appearance of things.
It was in a large part exposure to tribal art that allowed these pioneers to develop an entirely new aesthetic idiom.
Avant-garde artists became intrigued by Oceanic art.
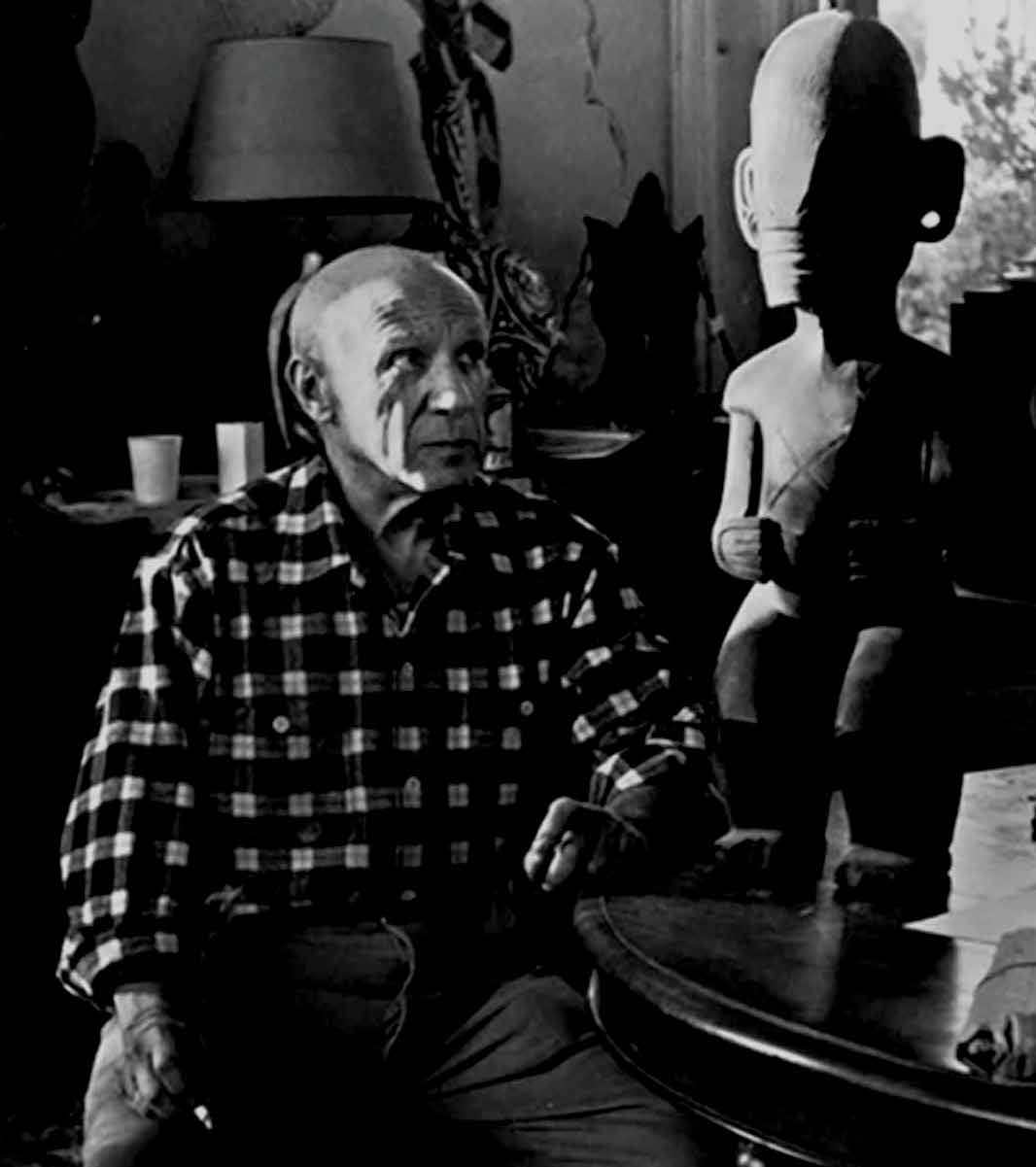

Picasso and his Marquesan Tiki
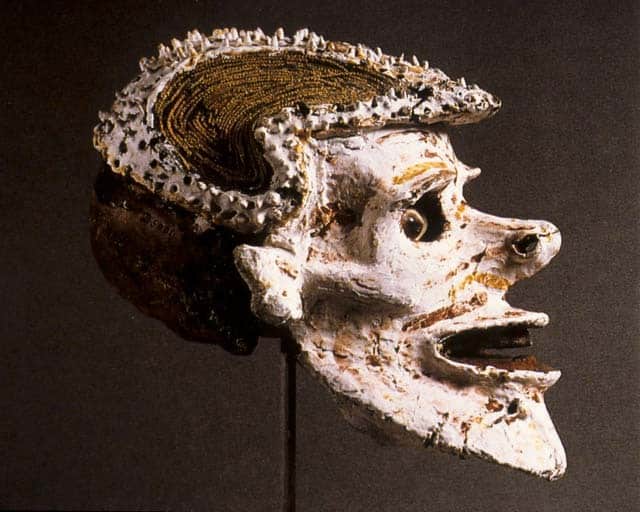
Overmodelled Skull New Ireland PNG
Inspiration or plagiarism
Giacometti would have seen this New Ireland over modeled skull in Basel during the 1940s. He was a regular visitor to that Swiss city’s great ethnographic museum. It is a fine line between creative adaptation and ‘artistic plagiarism’.
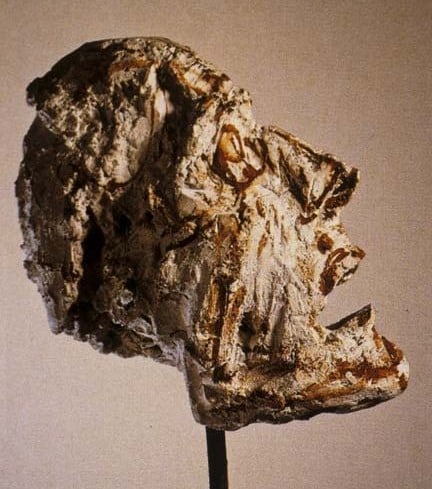


Vanuatu mask from Picasso collection
Color and form
In indigenous art the human figure is also depicted in radically different proportions from European art. The head is often disproportionately large. The organization of the body bears only an indirect relationship to its muscle and bone structure. It was different, unrealistic and yet it still worked.
Avant-garde artists realized color in Oceanic art was often integral to sculptural form. The removal of color would often radically alter the perceived ‘form’ of a carving.
In the first decade of the 20th-century avant-garde painters and sculptors applied its lessons from Oceanic art. Gauguin,even moved to the Pacific, first to Tahiti and later to the Marquesas. In doing so, he became the first great Western artist to live for a large part of his life outside Europe.
Another, illustrated by Gaugin but also many others including Surrealists such as Max Ernst and Matta, involved incorporating images and motifs of Oceanic origin into their own work. Major avant-garde artists even made adaptations in modern media of individual Oceanic pieces.
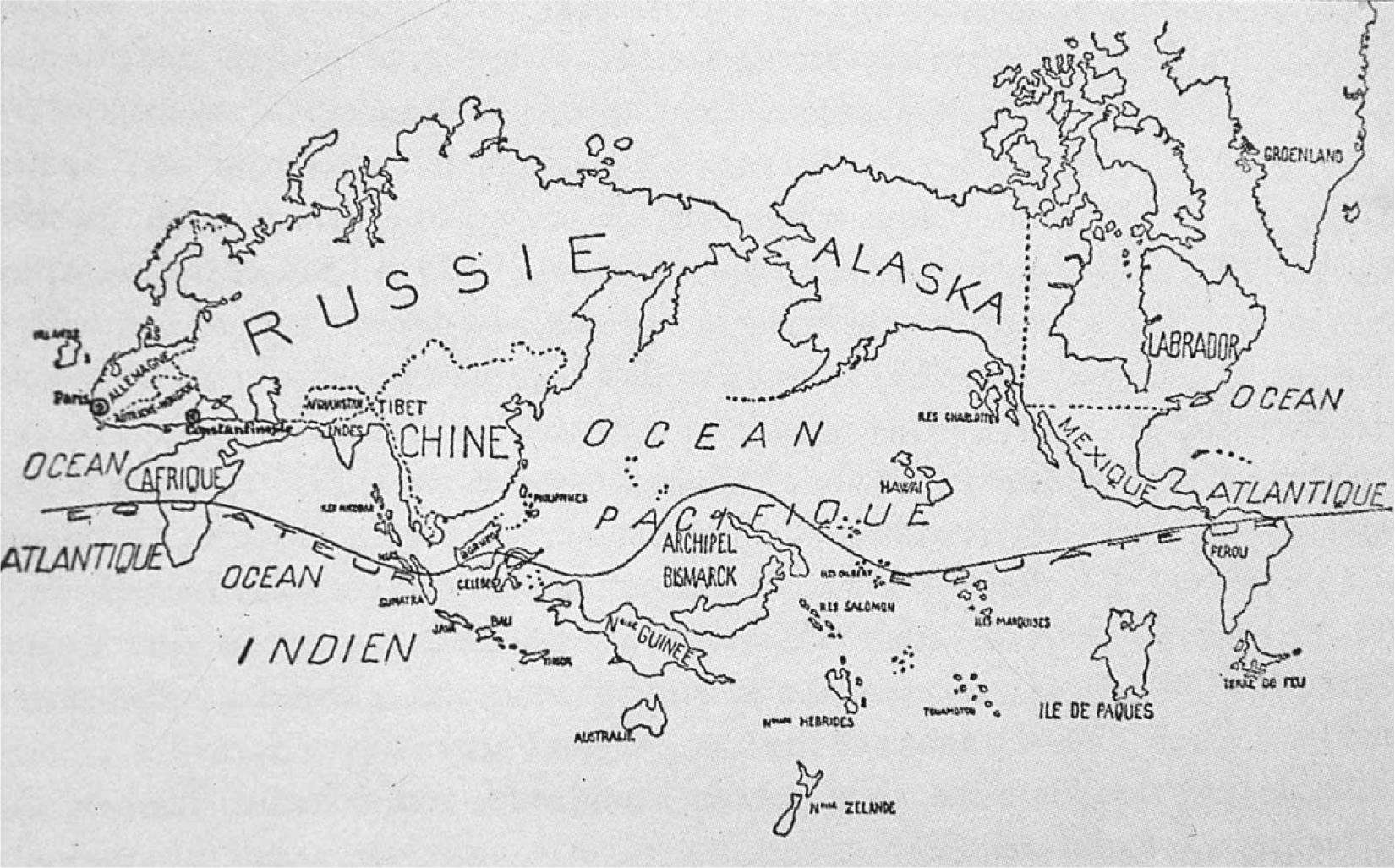
Surrealist Map of the World. Published in Variétés, 1929
The Surrealists, who rose to prominence in the 1920s, acknowledged their debt to the art of the Pacific. They produced a famous Surrealist Map of the World. This gives pride of place to the Pacific. The map represents the size of islands and continents not on the basis of their actual dimensions but according their art.
New Guinea and the adjacent islands of New Britain and New Ireland, as well as Easter Island predominate. Easter Island is only a speck on a conventional map, is larger than India to the surrealists
Oceanic Art by Area
Oceanic art from New Ireland PNG
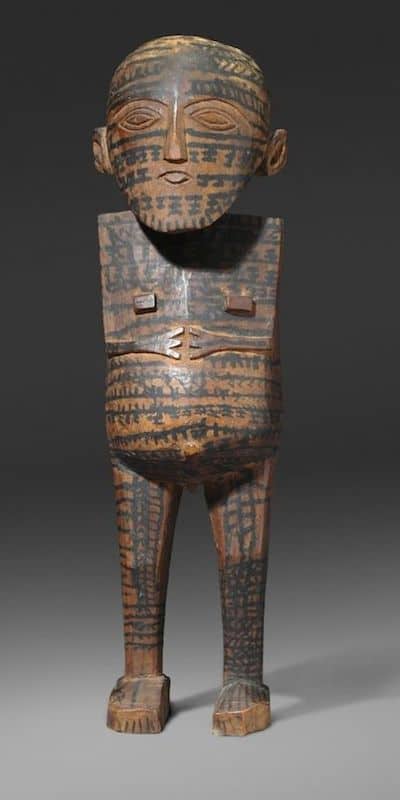
Malangan Sculptures
Malangan Figures come in a huge variety of styles but are all carved from a fairly soft wood. Typically they intensely painted in designs of Red white and black. They sometimes also have a small area of blue or yellow. The eyes made of a distinctive shell. Malangan come from the northern Regions of New Ireland
They are the only figures from new guinea that are sometimes made from more than one piece of wood. traditionally this form of tribal art was burnt after use.
Malangan culture also produced fantastic varieties of masks.


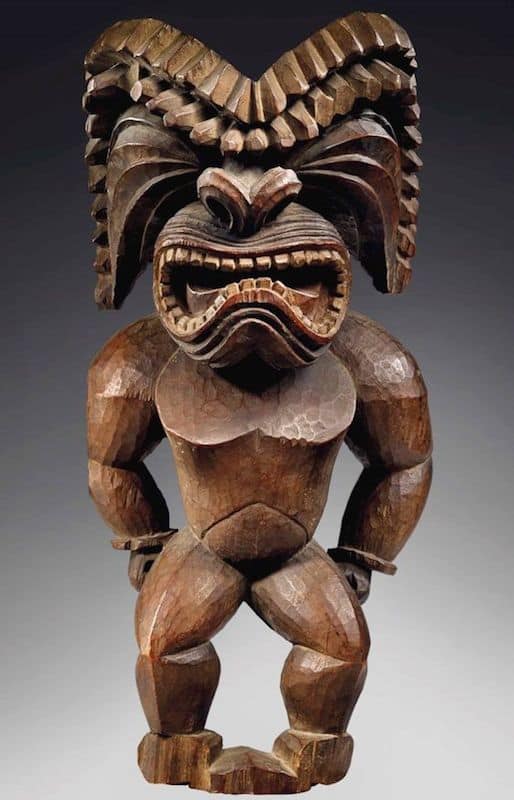
HawaiianArt
Hawaiian free standing sculpture made for tribal use is exceedingly rare. Only around 150 examples exist worldwide.
Sculptural Art tradition in Hawaii was directly linked to the islands traditional religion. In 1819 the island became Christian and the old gods destroyed and abandoned to rot.
The sculptures that remain from the pre-Christian era though are amongst the most powerful and collectible pieces of art


Cook Island Art

Oceanic Art from the Cook islands was of important Ancestral figures. These ancestors were often the first voyageurs to land on the Cook Islands. These ancestral sculptures were the main focus within the cultural enclosure.
The majority of Cook island Art was destroyed along with the temples shortly after the arrival of the London mission Society by 1821.
Cook island is also well known for their ceremonial Adze.

Austral Island Art

Austral Islands Sculpture
Very few freestanding sculptures exist from the Austral islands but the few that there are, are superb.
The islands are best known for its wonderfully carved Austral island Paddles and drums.
There are also a few very rare staff gods and wonderfully carved fly whisk handles

Austral island paddle terminal

Marquesan Art
Marquesas Islands Art
Free standing sculpture from the Marquesas islands is very rare. A Marquesan sculpture is normally a part of a utilitarian object.
The Marquesan islands also produced superb war clubs

Marquesan Polynesian Club



Solomon Island gourd stopper
Solomon Islands Art
The Solomon Islands lie to the South East of New Guinea in the Pacific Ocean. Culturally Nissan Island, Buka, and Bougainville are a part of the Solomon Island Art.
The two most renowned areas of Art production in the Solomon Islands are Roviana and Marovo. The Solomon islands have 67 language groups and each group was a tribe. Different tribes made different art objects. Not only does Solomon island art vary between language groups it also varies over time. Art changes with westernization through colonization and missionary actions.
The Solomon Islands used to be an area with both headhunting and cannibalism between waring island nations. Solomon islands Art reflects this with much of their art associated with canoes and warfare. If you are interested in knowing more about Solomon Islands Art it is covered in a separate article.
Easter Island Art
Easter Island Oceanic Art
Most people associate Easter Island Sculpture with their giant stone Moai. There are however lesser known small wooden sculpture which in my opinion are even more fascinating. Wooden Easter Island sculpture has Four main types.
Starved Male figures Moai Kavakava
Full bodied Male Figures Moai Tangata
Female Flat bodied figures Moai papa
Lizard – men hybrids Moko



Fijian oceanic art
Artistically Fiji has acted as a cultural bridge between Melanesia and Polynesia. The function of free-standing Sculpture within Fijian society unknown but most of the free-standing figures from Fiji are female. Fijian carvers are better known for making war clubs of which there are thousands of remaining examples.
Some figures are in the form of dishes used by “native priests”.
Fijian figurative sculpture tends to be rough and unrefined. It is however extremely rare so very collectible.


Sepik Art Papua New Guinea

The Sepik River is one of the greatest art producing areas in the world. There is such a variety of Sepik Figures and styles that it has its own article. The area has numerous different styles.
This is just a few examples




Tongan Art

Figurative sculpture from Tonga is very rare. Sculpture is done in hardwood or sperm whale Ivory.
Figures are female and have simple clean forms with superb clarity.

Oceanic Art from The Papuan Gulf

Imuni Figures are three dimensional and often carved from mangrove wood. Part of the charm is that the carver uses the natural woods shape when carving.
Flat figures from the Papuan Gulf are Bioma and older ones tend to have more fluid forms and often have a pierced nose.
Hohoa boards are often mistaken for shields. Even though they are flat they are actual figures that represent ancestral heroes. Nearly all have concentric circles for eyes. Old examples have raised noses and sometimes forehead.
Skull racks are very rare. They were to hang the skulls of dead enemies. They come in different styles but all have somewhere to hang skulls from.




Maori Oceanic Art

The New Zealand Maori were prolific sculpture artists and there are whole books on just Maori Art. Maori Sculpture and Maori Art will be in a separate article.


Oceanic Art
This is just some examples, so I hope you can appreciate the vast variety of oceanic art styles. The Pacific is probably the most prolific figure-producing region of the World after Africa. As oceanic art, they are extremely expressive and come in a vast variety of sizes forms and functions. It is a great pity that the majority of people who visit the Pacific only get to see the modern Tiki art produced for sale to tourists.
It would take a few very thick book to cover the whole of oceanic art and the best of these books include Art and Artefacts of the Pacific and Art of the Pacific There are about 100 more books on the subject
If you enjoyed this article you may also enjoy New Guinea sculpture and Antique tribal art
All images in this article are for educational purposes only.
This site may contain copyrighted material the use of which was not specified by the copyright owner.















